About wheels
Wheel is one of the components of a vehicle. To be able to fully perform their tasks, wheels should match tire type, as well as conditions of operation and maintenance. Conditions of use of a
wheel are primarily determined by the purpose for which vehicle is used.
Wheeled vehicles
Wheeled vehicles are classified by fields of application:
- passenger cars;
- medium-duty vehicles;
- off-road vehicles;
- buses and trolleybuses;
- forest and road cars;
- agricultural machinery.
Wheel rims also have their own classification. They are grouped into detachable and one-piece wheel rims. Detachable wheel rims consist of several elements, and one-piece are made of just one element. Type should be chosen depending on the field of use. For example, one-piece types are used for agricultural machinery, tractors and passenger cars. Such kinds of transport as trolleybuses, trailers, buses and trucks use both types of rims.
Wheels are also divided into the following types:
- Disk detachable products. They are primarily used for vehicles of medium and small capacity. These types of wheels are used with tires without tubes. There are options with detachable elements that are actively used in high capacity transport.
- Diskless types are used for high capacity vehicles. Wheels of this type can be detachable in longitudinal or transverse direction. Wheels without disks have several advantages. For example, they allow to increase load several times, as well as to extend service life of the product.
- Wide-profile wheels differ from other types primarily by almost twice the profile width, which
affects strength of bead section and carcass. This type of wheels is used mainly in off-road vehicles. - Products intended for pneumatic and arched tires ensure free passage for vehicles even in places where there is no quality road. There are two options of design of this product. The first option uses soft seal for bead section, the second option, hard one. The first option is more popular, that’s why you can find options with and without disks.
- Large-sized wheels are used for dump trucks with high load capacity. Tires will be attached to special type diskless wheels.
High demands are placed on production of wheels for tubeless tires — increased tightness and rigidity; due to this, they can withstand external influences.
Terms
Please, find below main terms used in this article:
Wheel is a unit that rotates and transmits the load. Location: between tire and hub. Main parts wheel consists of are disk and rim.
Disk is a wheel component connecting rim hub.
Rim is a wheel component used to mount tire.
Single wheel is a single wheel that is mounted on one hub.
Twin wheel is two different wheels that are mounted on the same hub.
Offset wheels (zero, positive or negative offset) are different types of wheels that may differ from each other by the way they are mounted on hub relative to the plane. In case of zero offset,
mating face will coincide with the central plane of rim rotation. In case of positive offset, there will be a certain shift towards vehicle longitudinal axis. Negative offset means shift from longitudinal axis. Offset specification can be found in technical documents or in product marking (“+” or “-“).
Disk wheel consists of disk and rim.
Diskless wheel: rim is attached to hub.
Compound wheel is a product that includes a part of rim and disk which are integrated into rim structure. There are also some disks that are welded to each part of rim.
Convertible wheel is a product which is connected through any part of disk with hub; this allows to provide negative or positive offset.
Adjustable wheel — rim is placed at distance L from disk, or the product includes turning component.
Wheel design
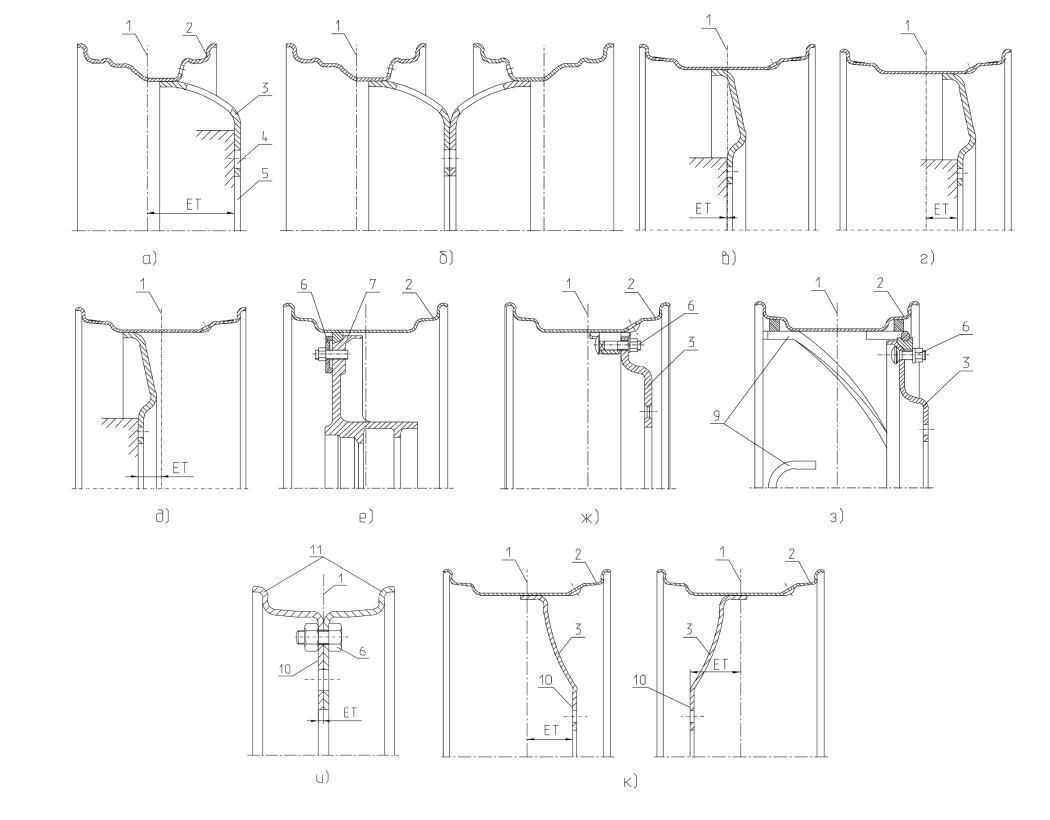
Figure 1.1 shows different types of wheels: A — single wheel, B — twin wheel, C, D and E — wheels with zero offset, + and -. Diskless wheel — F. Adjustable wheels are shown in G and H. The first letter corresponds to manual adjustment, the second one, adjustment with the help of turning component. Compound wheel is shown in figure I. J depicts convertible wheel.
Numerals also have meaning:
1 – track from hub rotation in central plane.
2 – direct rim.
3 – disk.
4 – holes with fasteners.
5 – central part.
6 – various fasteners.
7 – hub.
8 – direction of bracket.
9 – strips for screw tasks.
10 – disk mating face.
11 – flanges near bead sections.
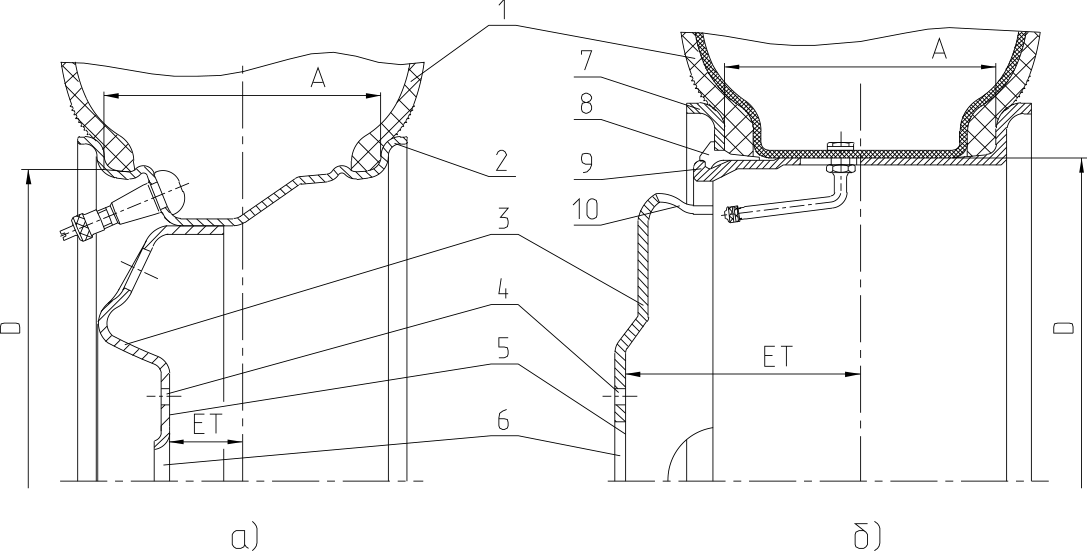
Fig. 1.2 shows main wheel parts.
Main components:
- Pneumatic tire (No. 1).
- Rim (No. 2).
- Disk (No. 3).
- Fastener holes (No. 4).
- Mating face (No. 5).
- Central hole (No. 6).
- Base ring (No. 7).
- Lock ring (No. 8).
- Base part of rim (No. 9).
- Ventilation holes (No. 10).
The figure shows two types of wheel: with single-piece (A) and detachable rim (B).
Basic characteristic of rim profile are as follows:
- diameter;
- width;
- ratio of flanges of beads.
Other criteria of wheels are:
- Wheel dimensions in the part that is used to connect it to hub. This value depends on such factors as diameter, location, number of holes in hub, diameter of central hole in disk as well as parameters of tapered and spherical bevel. Diameter of fasteners in disk influences product service life and weight. Standard dimensions also depend on the way they are centered on hub.
- Inter-center distances for twin wheels. Rim offset is a constant value almost for all wheel types, except for tractors. In this case, there are step-by-step and infinite methods of rim offset adjustment. Setting of rim offset is done manually or with the help of a turning element located in wheel. In the latter case, special strips are connected to rim; disk can freely move on these strips.
Wheel and rim marking
Major types of rims:
- Detachable rims. Their profile is either flat or angled (5º). Tires can be placed along beads and along the central part of tire.
- Single-piece rims. Profiles of this type can be either deep or very deep. They can be either symmetrical or not.
In order to identify marking of rims, it is necessary to understand what parameters can be included in marking. According to international and national regulations, main elements which are included in marking of rims are as follows:
- Types of rim profile.
- Form of bead flange and its height.
- Width of profile.
- Type of bead seats. These parameters can be added after specification of product diameter. Thus, symbols 5½Jх14Н (4½Jх13Н2, 6Jх15Н2) can designate profiles of
rim seat: Н – single-side, Н2 – double-side. They can be round, flat or combined. - Symmetry in profile is designated by S symbol. For example, marking 5½Jх14Н-S means that there is symmetry in rim.
- Information specifying whether rim is detachable or not. For example, if between symbols there is dash (-), it means that rim is detachable. For single-piece rims, symbol (х) is used.
- Rim diameter and width. These data are either in millimeters or inches.
Nowadays, designation of rims is standardized throughout European countries: the European Tyre and Rim Technical Organisation have accepted relevant standards. Ukrainian designation
standard is GSTU 3-010-2000.
Tractor single-piece rims make exception in designation rules. In order to make it clear which type of rim well is used, in front of main symbols there is either W, or DW code. The former
stands for deep well, the latter, for very deep.
According to the international standards, it is possible to indicate standard sizes in different order. In this case, data will be specified not in the common way. Standard size is usually
designated similar to the designation in the rim, which is included in it.


